Air Pollution

What is air pollution?
Air pollution, both in outdoor and indoor environments, refers to the presence of chemical, physical or biological agents that alter the natural composition of the atmosphere and may prove harmful to human health and the environment.
According to WHO data, almost the entire global population (99%) is exposed to air pollution levels that exceed recommended limits. Exposure is especially high in low- and middle-income countries.
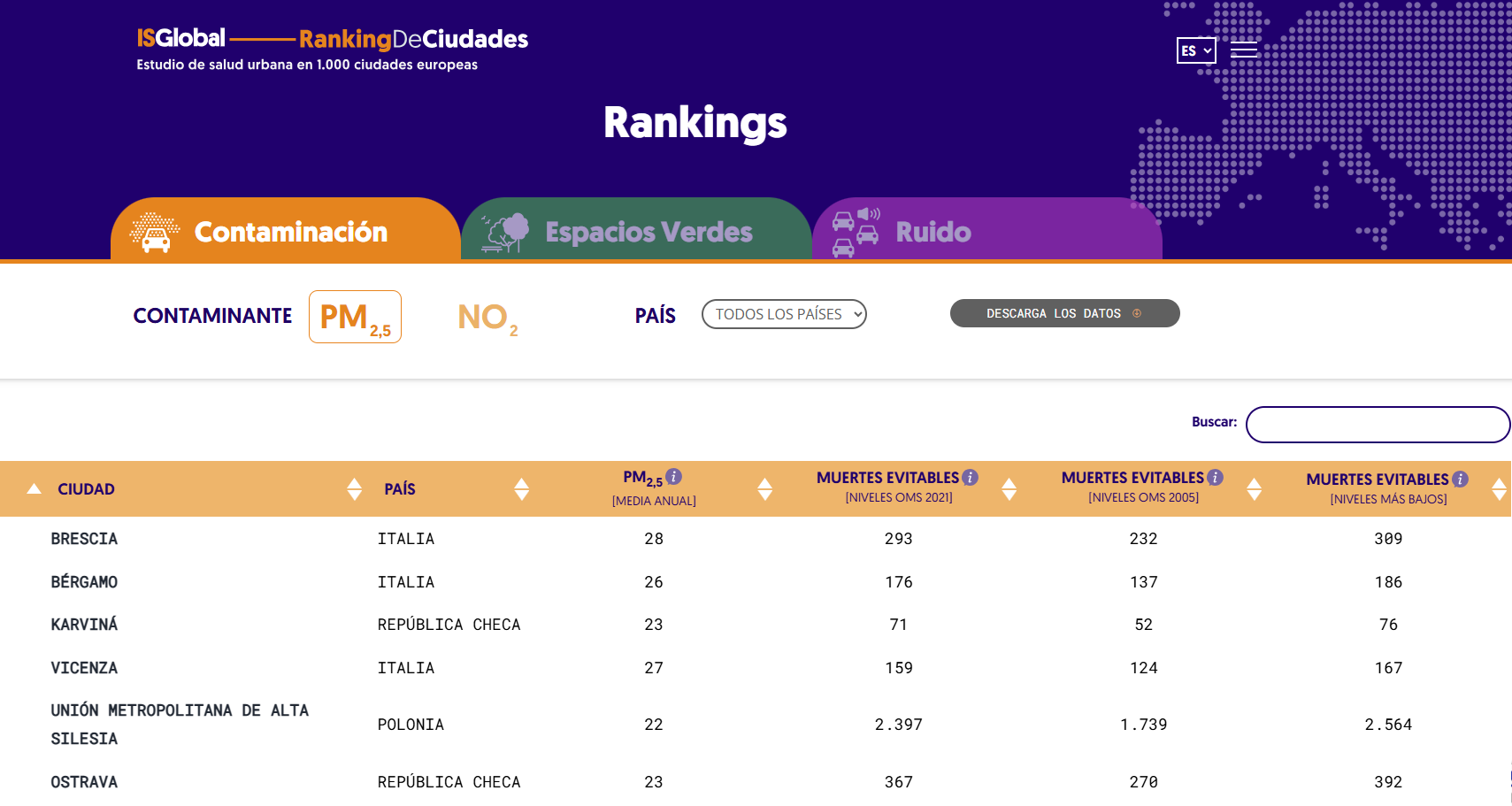
Sources of air pollution
Air pollution can have a natural origin or an anthropogenic origin, meaning it is caused by human activity.
- Examples of natural sources of air pollution include dust carried by the wind, volcanic eruptions, or wildfires.
- Among the human-made sources are motor vehicles —including maritime and air transport—, household activities involving any type of combustion (such as biomass burning, heating, or gas cooking), industrial facilities, agriculture, and wildfires caused by non-natural factors.
Types of pollutants
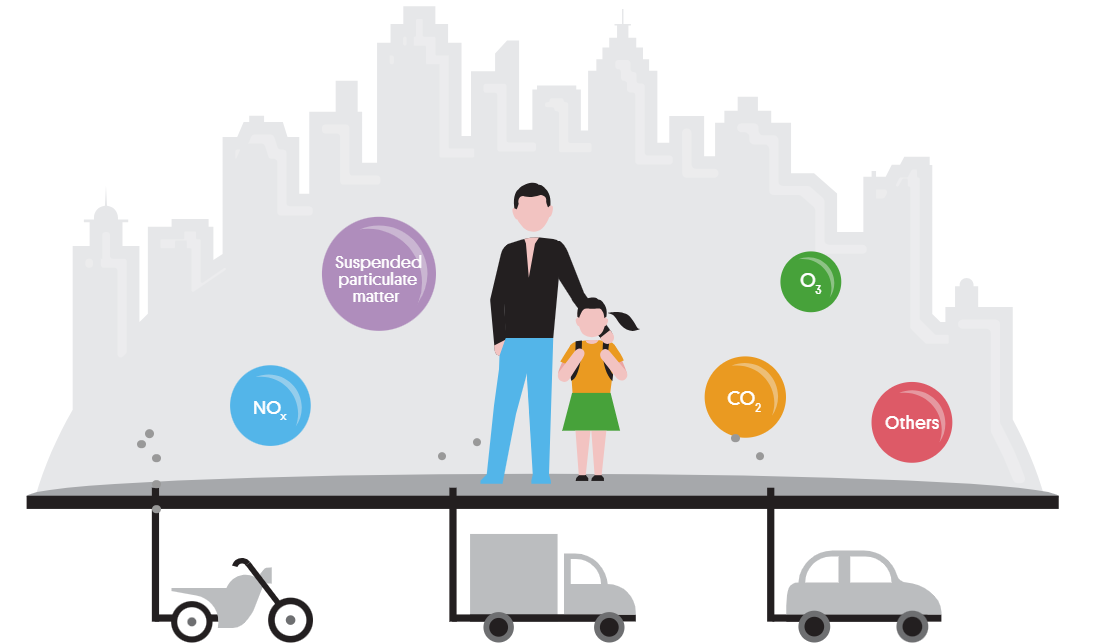
Air pollutants can be classified into two groups: primary pollutants, such as nitrogen oxides or NOx (nitric oxide or NO and nitrogen dioxide or NO₂), and particulate matter (PM), which are emitted directly into the atmosphere; and secondary pollutants, such as ozone, which form in the atmosphere through chemical reactions between primary pollutants.
The main pollutants include:
- Carbon dioxide (CO₂)
- Ozone (O₃)
- Nitrogen oxides (NOx): including nitric oxide (NO) and nitrogen dioxide (NO₂)
- Particulate matter (PM): includes coarse particles (PM10), fine particles (PM2.5), and ultrafine particles (PM0.1), depending on their diameter.
- Others: Carbon monoxide (CO), benzo(a)pyrene, benzene, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, methane, etc.
Consequences for human health
Air pollution, both outdoors and indoors, can lead to premature mortality and numerous diseases. A large body of scientific evidence links air pollution to asthma, COPD, lung cancer and other respiratory diseases, as well as an increased risk of stroke, neurodegenerative diseases, mental health issues, cardiovascular disease, and conditions affecting the reproductive system and foetal development, among others.
The most dangerous pollutants for human health are particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10), nitrogen dioxide (NO₂), carbon monoxide (CO), and ozone (O₃).
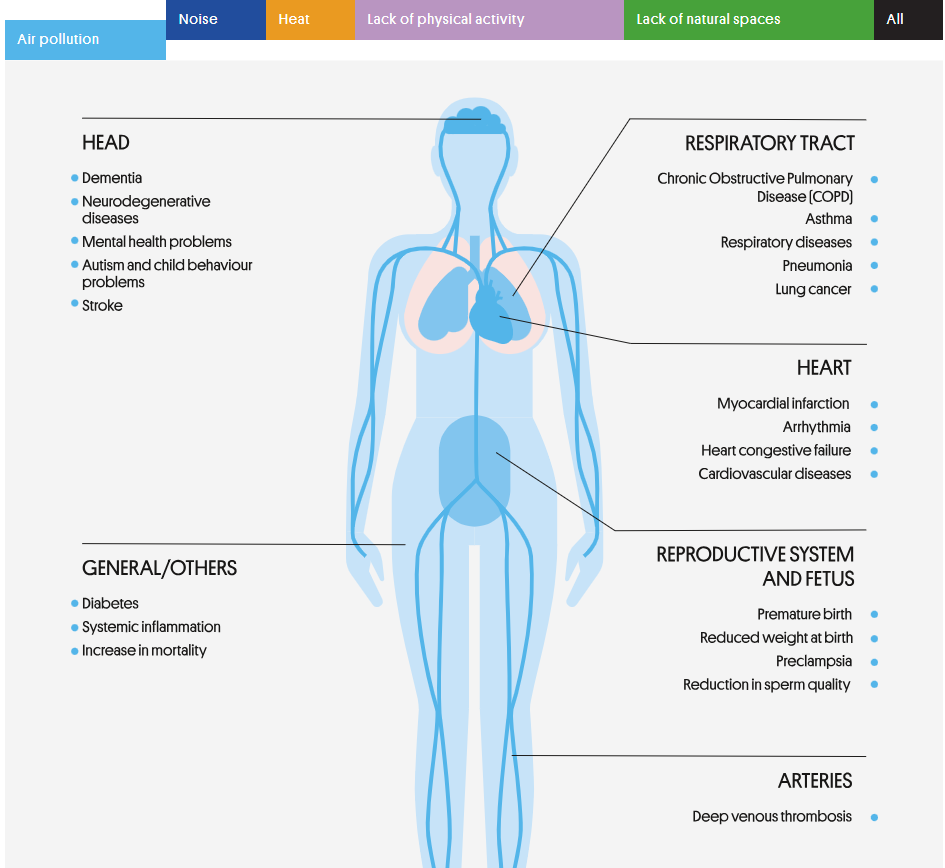
Effects of air pollution on health. Clicking on the image will take you to the interactive infographic.
Consequences for the environment and ecosystems
Air quality is closely linked to global climate and the health of ecosystems. Many sources of pollution, such as the burning of fossil fuels, emit not only greenhouse gases like CO₂ but also other substances that directly harm nature.
Pollutants such as tropospheric ozone affect crops and forests by reducing their growth and biodiversity. In addition, excess nitrogen in the air is deposited in soil and water, disrupting nutrient balances and encouraging invasive species. Soil and water acidification also causes toxicity for many forms of life. These impacts weaken ecosystems and jeopardise essential functions such as food production, climate regulation, and biodiversity conservation.
READ MORE
COLLAPSE
- Climate, Air Pollution, Nature and Urban Health(ISGlobal)
- Air Pollution and Children's Health. Let's Protect our Future Generation with Improved Ambient Air Quality Guidelines(ISGlobal, 2024)
- Transport, Domestic Activities and Agriculture are the Main Contributors to Air pollution Related Mortality in European Cities(ISGlobal, 2023)
- 33% of New Childhood Asthma Cases in Europe Attributable to Air Pollution(ISGlobal, 2019)
- Exposure to Air Pollution Before and After Birth May Affect Fundamental Cognitive Abilities(ISGlobal, 2019)
- Children who attend schools nearby traffic show a lower cognitive development(ISGlobal, 2015)
MULTIMEDIA MATERIAL