Ozone

What is ozone?
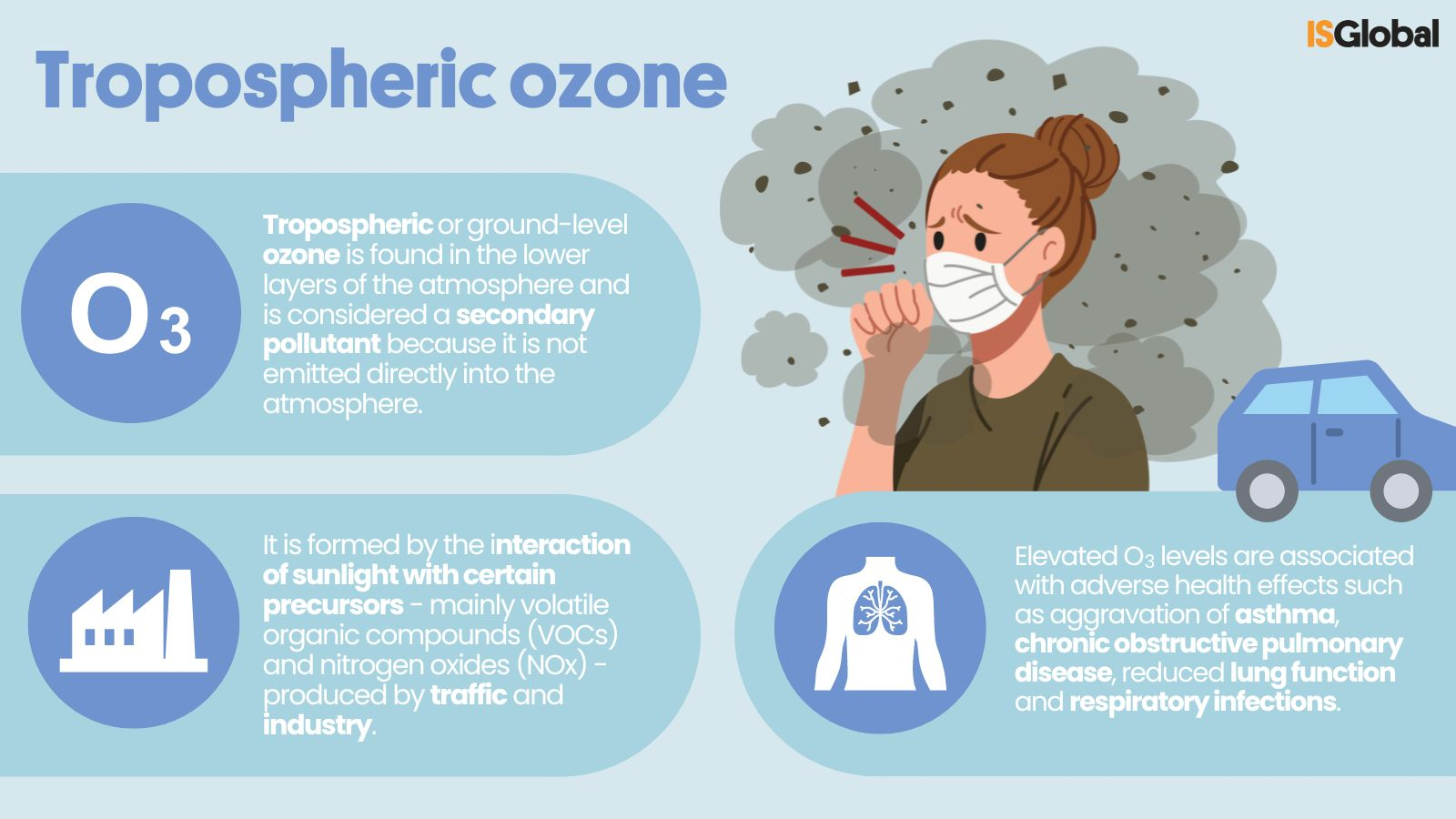
Ozone (O3) is a gas present in the atmosphere whose molecule consists of three oxygen atoms. In the stratosphere, at a height of between 10 and 50 km above the surface, it is an essential component for life on Earth. The ozone layer absorbs ultraviolet radiation from the sun, acting as a natural shield.
However, in the troposphere, the lowest layer of the atmosphere, ozone is a pollutant that poses a significant threat to human health and ecosystems.

Ozone sources
Atmospheric ozone is primarily formed through the interaction of sunlight with oxygen in the atmosphere. In contrast, tropospheric ozone is generated when solar radiation comes into contact with various precursor gases, mainly emitted by vehicles and industrial processes.
Consequences for human health
It is estimated that tropospheric ozone is responsible for one million premature deaths anually worldwide. In addition to coughing and throat and eye irritation, exposure to this pollutant can cause respiratory problems, such as aggravated asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, reduced lung function and respiratory infections.
Consequences for the environment
Tropospheric ozone traps heat in the lower atmosphere, so it also acts as a powerful greenhouse gas, contributing to global warming. It also reduces the ability of ecosystems to absorb CO₂, which has a negative impact on the climate.
Its effects also extend to vegetation. By penetrating plant leaves, tropospheric ozone reduces the efficiency of photosynthesis, slows plant growth and makes them more susceptible to pests and diseases. In ecosystems, high ozone concentrations can cause a loss of biodiversity and limit forest growth.
READ MORE
COLLAPSE
- Ozone, a Pollutant with Two Faces(ISGlobal, 2024)
- Air Quality in Europe Shows Significant Improvements over the Last Two Decades, Study Finds(ISGlobal, 2024)
MULTIMEDIA MATERIAL
