Greenhouse Effect

What is the greenhouse effect?
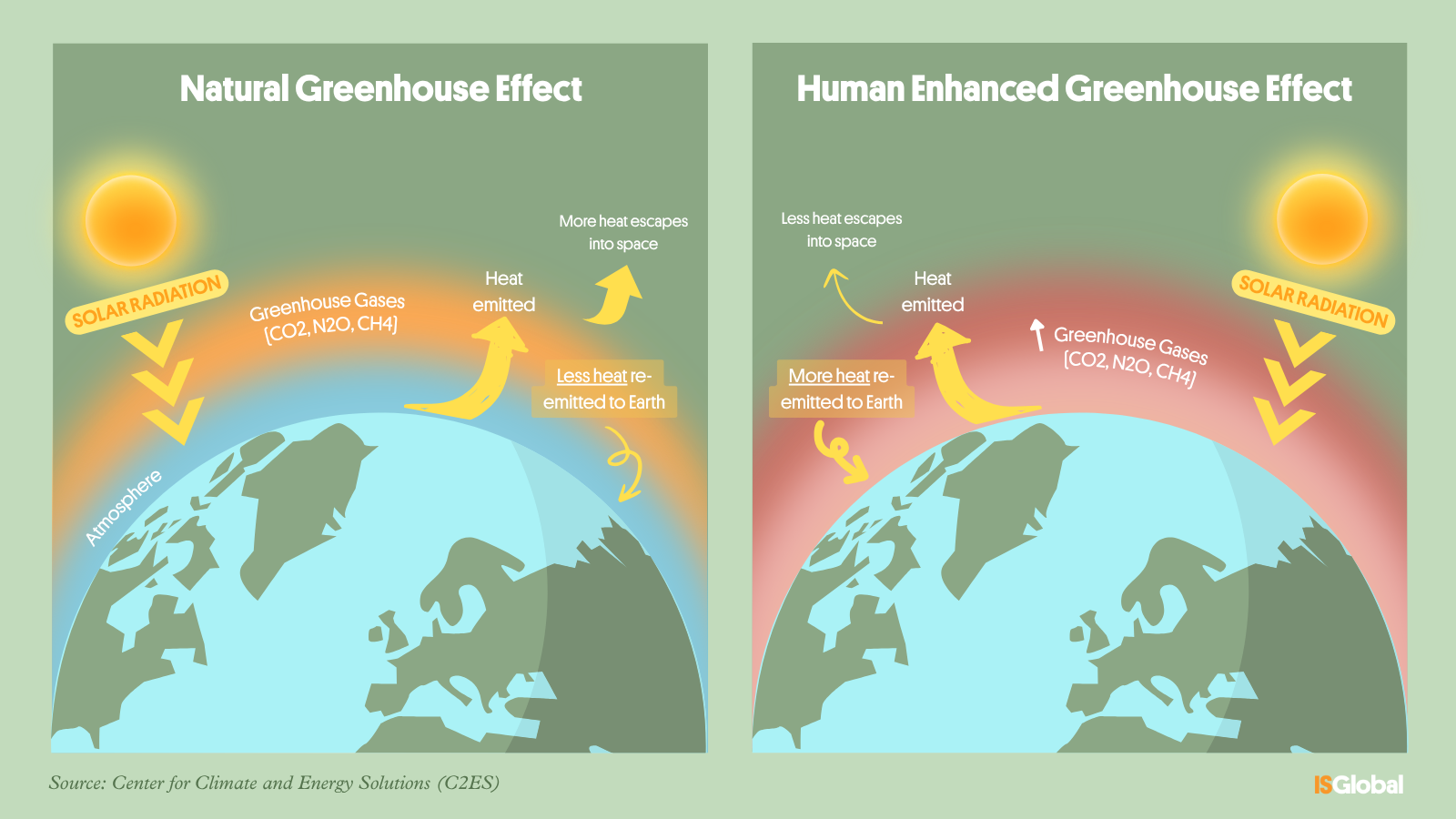
The greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon that allows the Earth’s temperature to be maintained within a range suitable for life. It is produced by the action of so-called greenhouse gases, which trap the heat emitted by the Earth’s surface after receiving solar radiation.
However, human activities have disproportionately increased the emissions of these gases since the beginning of the industrial era. This has intensified the greenhouse effect, leading to a progressive increase in temperatures known as global warming.
Main greenhouse gases
- Carbon dioxide (CO2): although it is also found naturally in the environment, CO2 produced by human activity is the main cause of global warming. It is mainly generated by the burning of fossil fuels (oil and derivatives, coal, wood, etc.).
- Methane (CH₄): generated during the production and transportation of fossil fuels such as coal, natural gas and oil. Also in livestock farming, as a result of the digestion processes of ruminant animals, in solid waste landfills, as a result of decomposition processes; or in rice cultivation, among other sources.
- Nitrous oxide (N₂O): this is produced in agricultural activities, such as the use of fertilizers and manure, and the burning of wood and fossil fuels. It also has industrial uses. Colloquially, it is known as “laughing gas” and is also used as an anesthetic in the medical field.
- Fluorinated gases: these are gases that are used in industry. They produce a greenhouse effect much stronger than CO2, although their proportion in the atmosphere is much lower. The most common are hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), used in refrigeration and air conditioning systems, among other applications.
- Water vapour (H₂O): this is also a greenhouse gas, although in this case it is of natural origin.
Sources of greenhouse gases
Among the main causes of the increase in greenhouse gas emissions as a result of human activity are the use of fossil fuels, deforestation and certain industrial and agricultural processes. The burning of coal, oil and gas releases large amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2), while the felling and burning of forests reduces the planet’s capacity to absorb it. On the other hand, agriculture and livestock farming generate other gases that also contribute to the problem, such as methane produced by livestock and rice cultivation in irrigated conditions.
In addition, some industries release artificial compounds that remain in the atmosphere for a long time, enhancing global warming. Even wastewater treatment and the use of certain chemicals aggravate the situation.
Environmental consequences
Although the greenhouse effect is a natural and essential process for life, the excess emissions caused by human activity are disrupting this balance, accelerating climate change and creating increasingly visible impacts on the planet.
The greenhouse effect is causing a rise in global temperatures and triggering major changes in the Earth’s climate. These include polar ice melt, rising sea levels and altered rainfall patterns, which disrupt the water cycle. In addition, many species are being displaced or driven to extinction as their habitats are transformed.
Human health consequences
Rising temperatures are already having a direct impact on human health, as high temperatures trigger effects such as heat stroke, hyperthermia and the worsening of pre-existing health conditions, and are linked to an increase in mortality rates. It is estimated that heat-related deaths will increase over the coming decades.
Furthermore, according to the World Health Organization (WHO), climate change associated with the greenhouse effect contributes to the spread of diseases such as malaria, salmonellosis and various intestinal infections, especially in children. This is because the increase in temperatures allows the vectors that transmit these diseases (such as certain mosquitoes) to thrive in places where they were not viable before.
Likewise, it is predicted that the increase in the frequency and magnitude of climatic events will have a direct impact on mortality.
READ MORE
COLLAPSE
- Reducing Traffic in Barcelona by 25% Would Prevent Around 200 Premature Deaths a Year Linked to Pollution(ISGlobal, 2025)
- Compact cities have lower carbon emissions, but poorer air quality, less green space and higher mortality rates(ISGlobal, 2024)
- Transport, Domestic Activities and Agriculture are the Main Contributors to Air pollution Related Mortality in European Cities(ISGlobal, 2023)
- Greenhouse gases surged to new highs in 2023, warns UN weather agency(ONU, 2023)
