Carbon Dioxide (CO2)

What is CO2?
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is an odourless, colourless, tasteless and non-flammable gas. It is one of the main greenhouse gases and is vital for the life cycle. However, its excess in the atmosphere contributes to global warming and climate change. At normal temperature and conditions (at one atmosphere and 0 ºC), it is in gaseous form. It is composed of one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms.
Where does it come from?
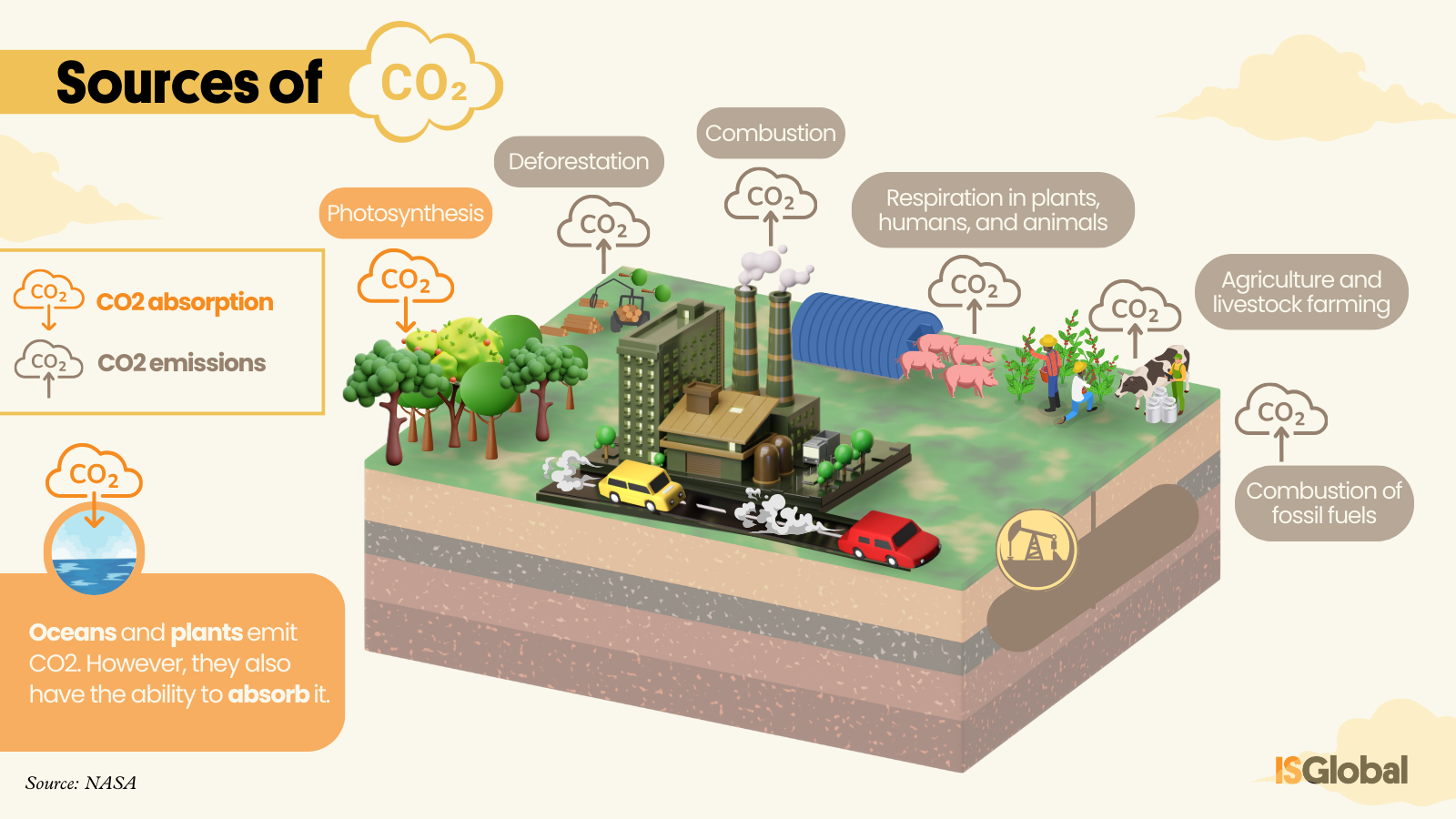
CO2 has two sources. On the one hand, it is produced naturally through processes such as the breathing of humans and animals, the decomposition of organic matter (for example, plants and trees) and the activity of oceans and volcanoes. In the same way, both the oceans themselves and plants during photosynthesis have the capacity to capture this gas, thus contributing to the regulation of the natural carbon dioxide cycle.
The second source of CO2 emissions is human activity, such as the burning of fossil fuels, agriculture and livestock farming, and certain industrial processes. Deforestation also contributes to a greater presence of CO2 in the atmosphere, since eliminating forests also reduces the planet’s capacity to eliminate this gas.
A greenhouse gas
Carbon dioxide is essential for the balance of ecosystems and life on Earth. It is one of the main greenhouse gases, which means that it has the capacity to trap heat in the Earth’s atmosphere. This phenomenon is essential for life on Earth, as it acts as a thermal layer that helps maintain a temperature suitable for life, among other functions. However, when there is an excess of these gases in the atmosphere, the greenhouse effect intensifies, causing the temperature to rise and leading to global warming.
Over the last few decades, CO2 levels in the atmosphere have increased uncontrollably due to human activity. This intensifies the greenhouse effect, causing more heat to be trapped and the global temperature to rise. This phenomenon, called global warming, has several serious consequences, such as an increase in the frequency of extreme weather events, disruption of biodiversity and impacts on human health, among many others.
READ MORE
COLLAPSE
MULTIMEDIA MATERIAL
